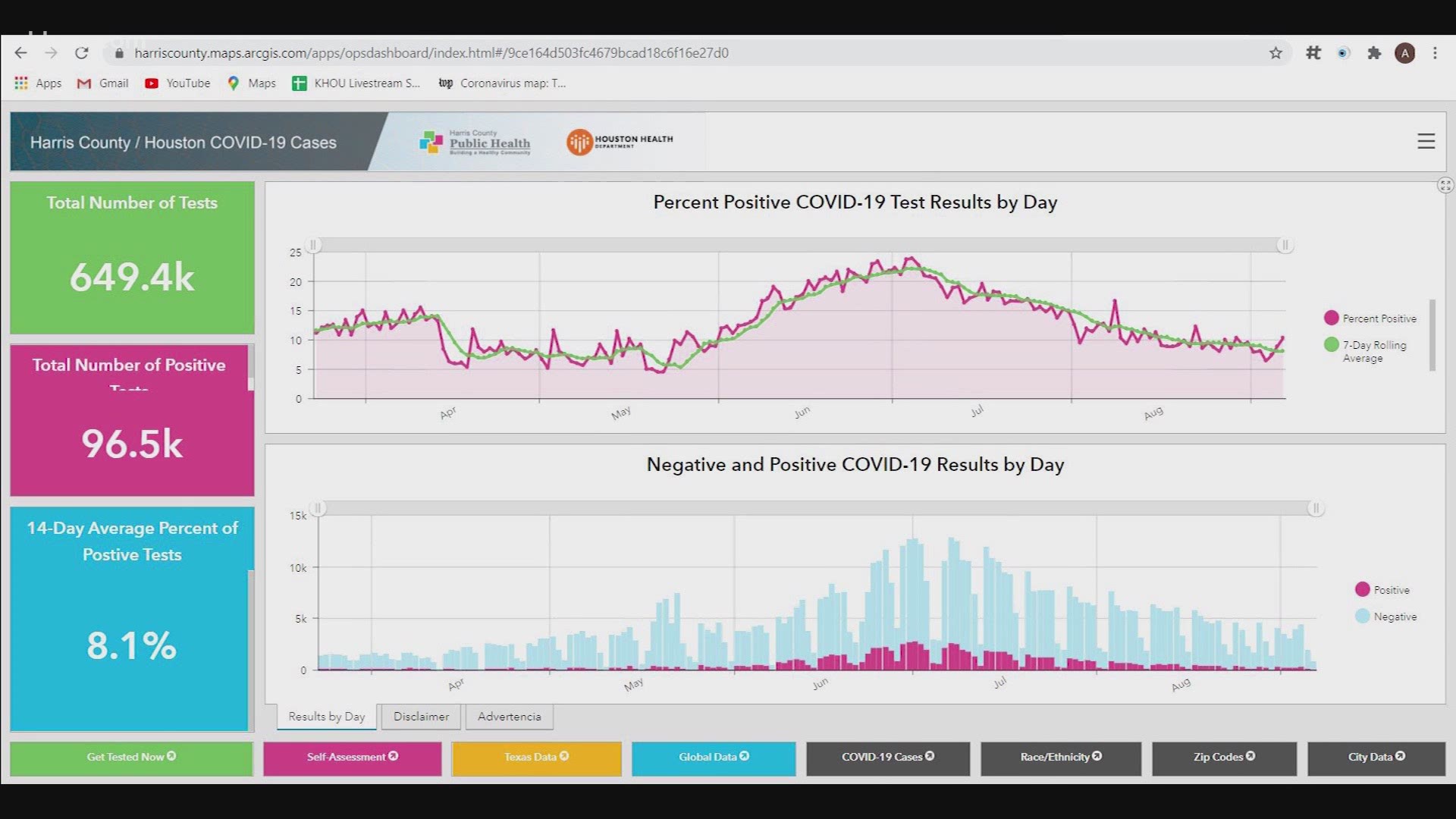
Texas health officials announced Monday that they are changing the way the state reports a key metric used to evaluate the extent of coronavirus infection. The state admits its previous method of calculating the “positivity rate” muddied the extent of viral transmission by mixing old data with new, the Texas Tribune reports.
The Texas Department of State Health Services said it will now “primarily rely” on a new calculation of the daily positivity rate — defined as the share of tests that yield positive results — that takes into account the date on which a coronavirus test was administered.
It also means that each day’s positivity rate will be an oft-changing number, fluctuating as officials collect lab results over time. Labs and hospitals report their test results to the state with varying degrees of timeliness, and state officials will have to recalculate the positivity rates for previous days as more test results from those dates pour in.
That’s a departure from the current system, which calculates the positivity rate based on the date the health agency receives test results, which can be weeks or even months after the tests were administered.
It marks the latest in a series of data methodology changes and corrections health officials have issued over the course of the pandemic.
While touting the new reporting method as an improvement, state officials defended the old system as providing the best information that was available at the time. The new positivity rate for the most part closely resembles the old metric, particularly when viewed as a trend line over time, officials said.
Health department spokesperson Chris Van Deusen said in an email that the different positivity rates generally moved in parallel until about August, when the state reported dumps of test results. “As long as the test results and new cases were reported fairly close in time, the case reported date was working as a metric,” he said.
Asked if the health department had concerns about the accuracy of the positivity rate before August, Van Deusen said, “We have to go off of the data that we have.”
The state said it will begin releasing the positivity rate under both the new and old methods later Monday. Health officials said they will publish a third positivity rate metric, which is calculated based on when lab results were reported to a national disease surveillance system, NEDSS, which officials said would reduce reporting lag time.
In its announcement, the Texas Department of State Health Services said the new calculations for the positivity rate will provide a more accurate representation of coronavirus transmission on any given day. It said the change was made after technology improvements last month improved the department's ability to use data from labs and other testing sites. The agency said that until recently, it wasn’t able to track test results by the date they were administered.
The state can now process about 100,000 lab reports per day, officials said, compared with about 45,000 per day before August.
“The numbers that we see from the county health departments or the state health department … they're not useless, but they are highly qualified and unreliable in terms of studying the trend,” Rajesh Nandy, associate professor of biostatistics and epidemiology at the University of North Texas Health Science Center at Fort Worth, has said.
Coronavirus test results vastly undercount the extent of viral transmission; researchers estimate that the true number of coronavirus cases could be more than 10 times the number of positive tests. As many as half of the people who contract the virus may never experience symptoms and may not seek out testing.
Texas health officials said Monday that the positivity rate is just one of many metrics that inform disease surveillance. After a midsummer surge that overwhelmed some Texas hospitals, particularly in South Texas, the state’s number of coronavirus hospitalizations has fallen in August and September. Still, rates of viral spread and hospitalizations are higher now than they were before Abbott began the phased reopening of businesses in May. More than 14,000 Texans have died from the virus, according to the state’s accounting.
The decision to start calculating and posting the additional positivity rates began this summer, when thousands of backlogged tests were added to the health department’s reporting system, causing the positivity rate to spike, health department officials said.
Part of that logjam — some 350,000 of more than 850,000 tests — had accumulated because the state could not process enough test results each day before an Aug. 1 system upgrade. Labs have also struggled to upload their test results to the state’s system, with formatting errors and glitches as minor as an errant question mark sometimes causing monthslong delays. Local officials and lawmakers have called the data “meaningless” and “inaccurate.”
The story comes to us from our news partners at the Texas Tribune. Read more more.